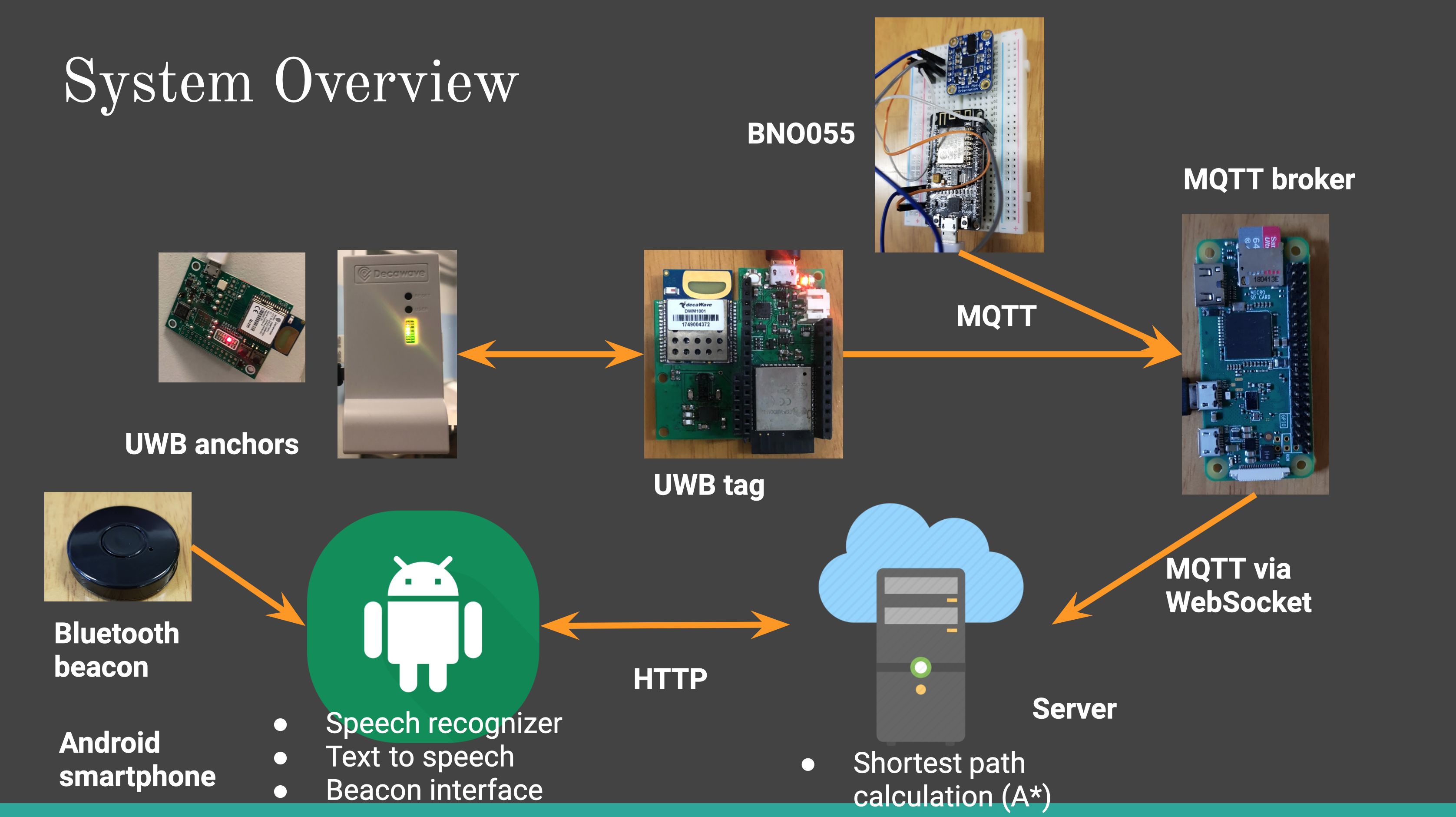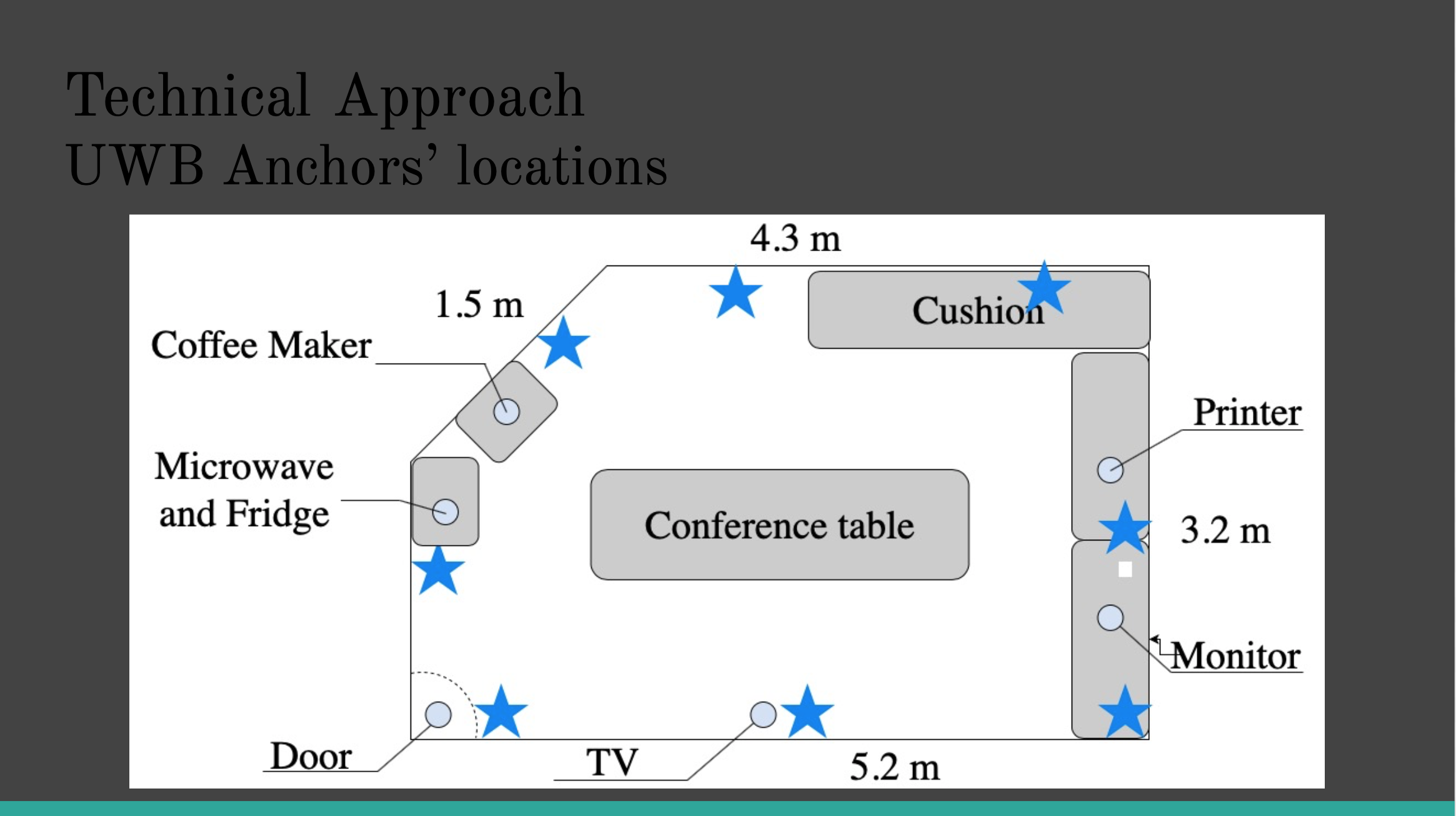
Motivation
Autonomous navigation is a crucial component for visually impaired people. Outdoors, positioning based on ubiquitous signals is feasible; however, for indoors, no universal positioning solution does exist. Due to the remarkably broad bandwidth, ultra-wideband (UWB) signs offer a proper multipath resolution and allow positioning with sub-meter (10 centimeter) accuracy. Also, because of the implementation of screen-reader software into mobile devices, visually impaired people nowadays can easily use smartphones. Having these two elements in mind, we decided to come up with a method of guiding blind people in indoor places.